Waste to Energy Plants in the US: Transforming Waste into Power
Introduction to Waste to Energy Plants
Waste to energy (WtE) plants represent a significant stride in sustainable waste management and energy production. As the United States grapples with increasing waste production, these facilities offer a dual solution: reducing landfill use while generating electricity. By converting waste materials into usable energy, WtE plants help mitigate environmental impacts and contribute to the energy grid. This article delves into the workings, benefits, and challenges of waste to energy plants in the U.S., highlighting their role in the broader context of sustainable development.
The Technology Behind Waste to Energy
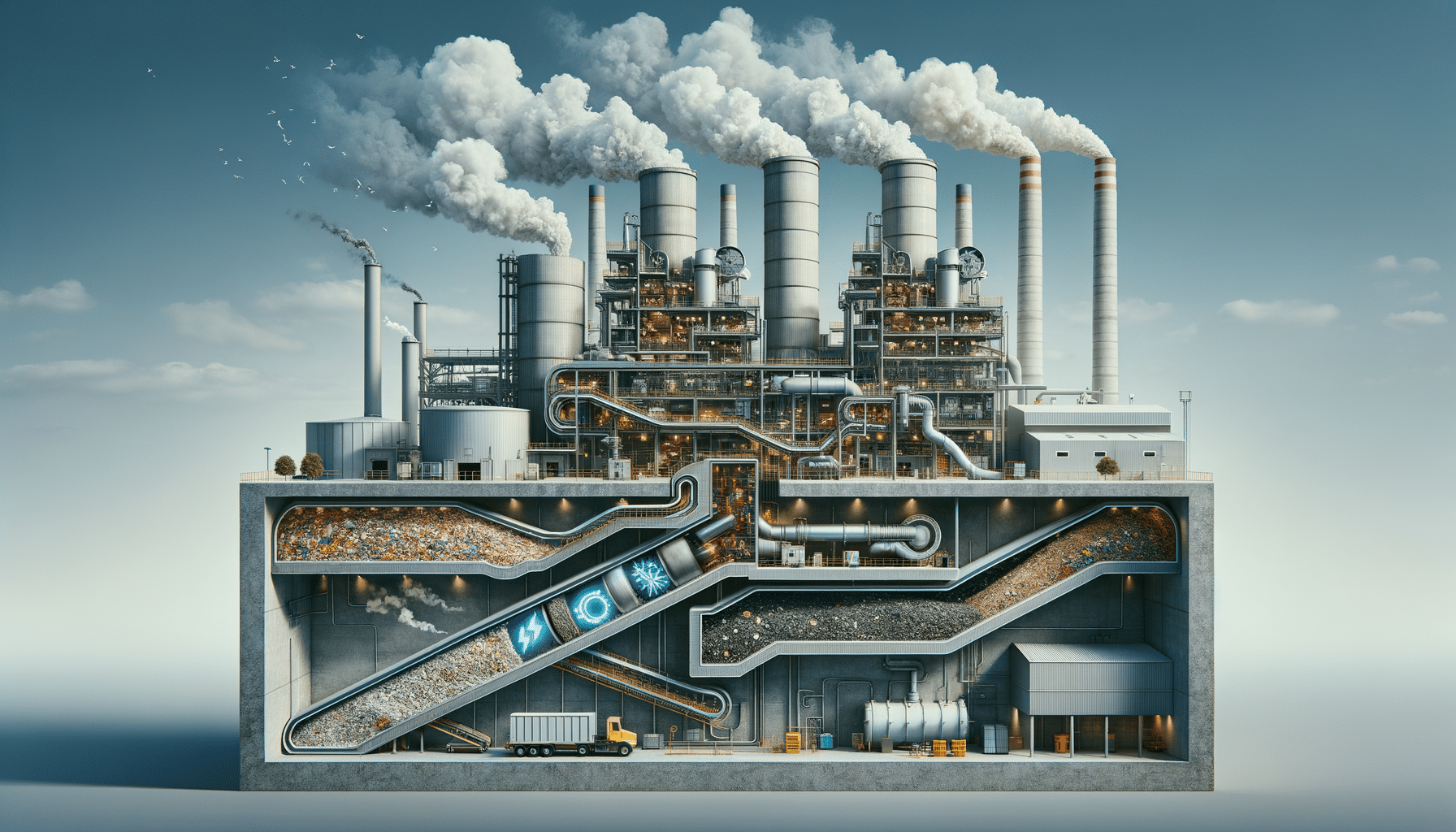
At the heart of waste to energy plants is the technology that enables the conversion of waste into electricity. The process typically involves the combustion of municipal solid waste (MSW) at high temperatures. This combustion process generates steam, which powers turbines to produce electricity. Advanced air pollution control systems are employed to minimize emissions, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Several technologies are utilized in WtE plants, including:
- Incineration: The most common method, where waste is burned to produce heat.
- Gasification: Converts waste into synthetic gas through partial combustion.
- Pyrolysis: Decomposes organic material at high temperatures in the absence of oxygen.
Each of these technologies has its advantages and challenges, influencing the choice of method based on local waste composition and regulatory requirements. The integration of these technologies into energy systems reflects a commitment to innovation in renewable energy sources.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Waste to energy plants offer numerous environmental and economic benefits. Environmentally, they reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills, thus lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with waste decomposition. By converting waste into energy, these plants contribute to a reduction in fossil fuel reliance, supporting cleaner energy production.
Economically, WtE plants can generate revenue through energy sales and tipping fees for waste processing. They also create jobs in plant operation and maintenance, contributing to local economies. Additionally, the reduction in landfill use can result in cost savings for municipalities, as less space and fewer resources are needed for waste management.
Despite these benefits, the economic viability of WtE plants depends on factors such as waste availability, energy prices, and regulatory frameworks. Strategic planning and investment are crucial to maximizing their potential.
Challenges and Criticisms
While waste to energy plants offer significant benefits, they are not without challenges and criticisms. One major concern is the emission of pollutants, including dioxins and heavy metals, during waste combustion. Although modern plants are equipped with advanced filtration systems, the potential environmental impact remains a point of contention.
Critics also argue that WtE plants may discourage recycling efforts by providing an alternative to waste reduction. The balance between recycling and energy recovery is crucial to sustainable waste management. Furthermore, the high initial costs of establishing WtE facilities can be a barrier for many communities, requiring substantial investment and long-term commitment.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing innovation and adherence to stringent environmental standards, ensuring that WtE plants contribute positively to sustainability goals.
The Future of Waste to Energy in the US
The future of waste to energy plants in the United States looks promising, with potential for growth and innovation. As technology advances, the efficiency and environmental performance of these plants are expected to improve, making them a more attractive option for waste management and energy production.
Policy support and public awareness are vital to the expansion of WtE facilities. Government incentives and regulations can drive investment and development in this sector, aligning with broader environmental and energy objectives. Additionally, increasing public understanding of the benefits and limitations of WtE plants can foster community support and participation.
In conclusion, waste to energy plants represent a crucial component of a sustainable future, offering a viable solution to waste management challenges while contributing to renewable energy goals. Their continued development and integration into energy systems will play a key role in shaping a more sustainable and resilient energy landscape in the United States.