Learn more about the usage of table saws
Introduction to Table Saws
Table saws are a cornerstone in woodworking, offering precision, power, and versatility to both hobbyists and professionals alike. These tools are indispensable for cutting large sheets of wood, making rip cuts, cross cuts, and various complex cuts with ease and accuracy. Understanding the usage of table saws can significantly enhance your woodworking projects, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Recognized for their ability to handle a variety of materials, table saws are also adaptable, with features that cater to different cutting needs. Whether you’re crafting furniture or constructing a new deck, a table saw is a tool that can transform your approach to woodworking.
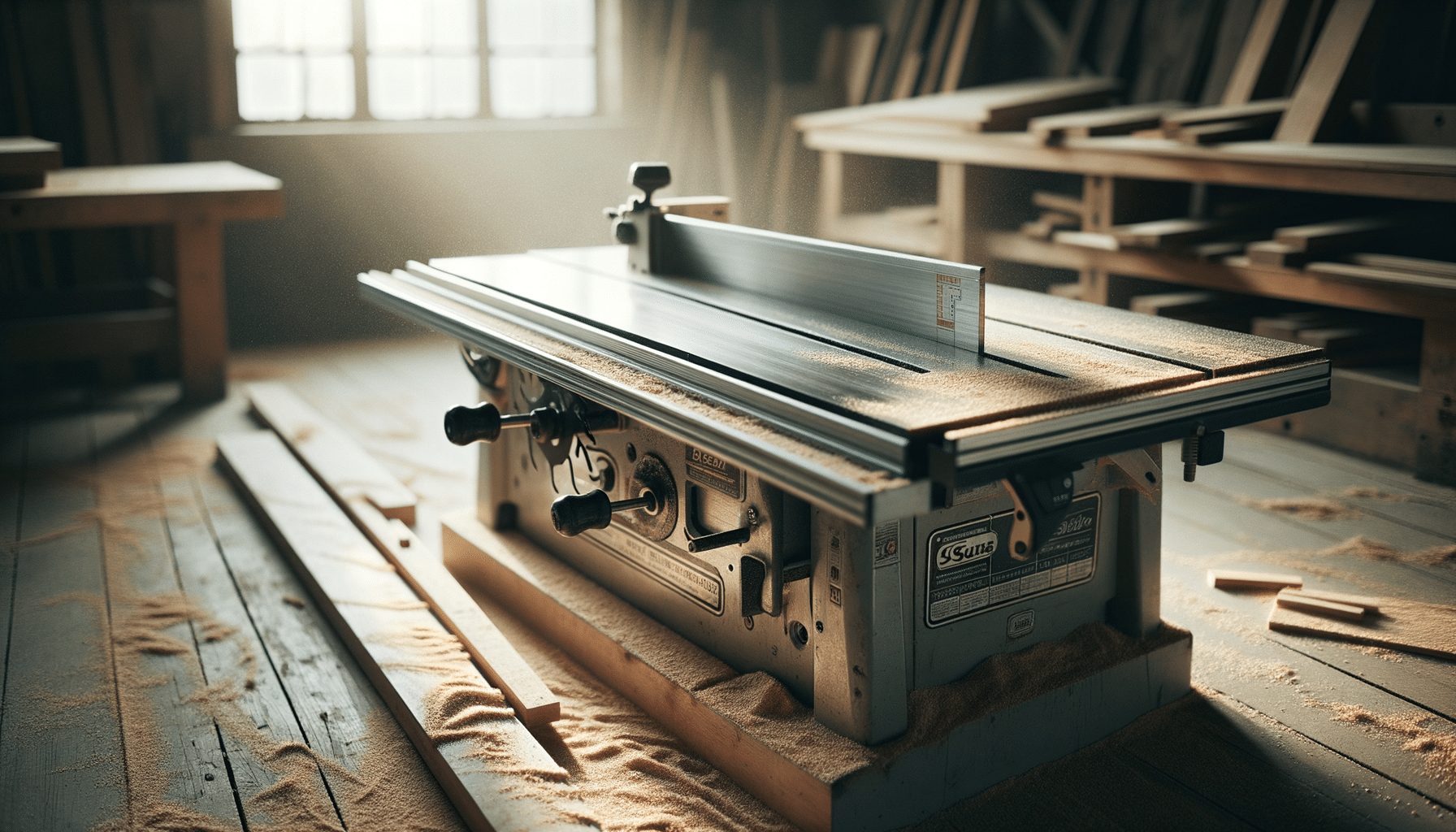
The Anatomy of a Table Saw
To fully grasp the usage of table saws, it’s essential to understand their structure. A typical table saw comprises several key components:
- Tabletop: The flat surface where materials are placed for cutting. It’s crucial for stability and accuracy.
- Fence: A guide that ensures straight cuts. It can be adjusted to accommodate different widths.
- Blade: The cutting element, available in various types for different materials and cuts.
- Motor: Powers the blade, with varying horsepower depending on the saw’s intended use.
- Bevel System: Allows the blade to tilt for angled cuts.
Each component plays a vital role in the functionality of the saw, and knowing how to adjust and maintain these parts can lead to more precise and safer woodworking.
Types of Cuts Achievable with Table Saws
Table saws are renowned for their ability to execute a wide range of cuts, enhancing the versatility of any woodworking project. Some of the most common cuts include:
- Rip Cuts: These are cuts made along the grain of the wood, ideal for resizing planks.
- Cross Cuts: Made across the grain, these cuts are perfect for shortening pieces to the desired length.
- Miter Cuts: Angled cuts typically used for creating frames and other decorative edges.
- Bevel Cuts: Similar to miter cuts but angled across the thickness of the material.
- Dado Cuts: Grooves cut into the surface of the wood, often used for joints.
Mastering these cuts requires practice and an understanding of the saw’s settings, but once mastered, they open up a world of creative possibilities.
Safety Practices When Using Table Saws
Safety is paramount when operating table saws. These powerful tools can be dangerous if not used correctly. Here are some essential safety practices:
- Wear Appropriate Gear: Use safety goggles, ear protection, and avoid loose clothing.
- Check the Blade: Ensure the blade is sharp and properly aligned before use.
- Use Push Sticks: These tools help keep your hands away from the blade while cutting.
- Keep the Area Clean: A clutter-free workspace reduces the risk of accidents.
- Understand the Saw’s Features: Familiarize yourself with the saw’s safety mechanisms, such as blade guards and emergency stops.
By adhering to these practices, you can minimize risks and focus on achieving accurate cuts.
Choosing the Right Table Saw for Your Needs
Selecting a table saw depends on your specific requirements and budget. Here are some factors to consider:
- Type of Work: For heavy-duty tasks, a cabinet saw might be more suitable, while a portable saw is great for smaller projects.
- Space Availability: Consider the space in your workshop; larger saws require more room.
- Budget: Prices vary widely, so it’s important to find a saw that offers the features you need within your budget.
- Features: Look for features such as dust collection ports, adjustable fences, and safety enhancements.
Carefully evaluating these factors will help you choose a table saw that enhances your woodworking endeavors.


